Mastering Cross-Site Request Forgery CSRF in TypeScript-Based ERP
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is a notorious security vulnerability that affects web applications, including modern ERP systems built with TypeScript. This blog delves deep into how CSRF attacks exploit trusted user credentials, how to prevent them in TypeScript-based ERPs, and provides practical examples for developers.

What is Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)?
CSRF tricks an authenticated user into performing unintended actions on a web application. It can cause data manipulation, unauthorized transactions, or access to sensitive information. In ERP systems, where sensitive financial and operational data resides, preventing CSRF attacks is critical.
Understanding Cross-Site Request Forgery CSRF in TypeScript-Based ERP
A typical CSRF attack occurs when:
- A malicious actor crafts a request and tricks the user into executing it.
- The browser automatically sends user credentials (e.g., cookies, tokens) with the request to the server.
- The server processes the request without verifying its authenticity.
Below is an example of a CSRF vulnerability in a TypeScript-based ERP system:
Example 1: CSRF Attack Scenario
// Vulnerable endpoint in an ERP system
app.post('/updateUser', (req, res) => {
const { userId, role } = req.body;
if (!req.isAuthenticated()) {
return res.status(401).send('Unauthorized');
}
updateUserRole(userId, role); // No CSRF validation here
res.status(200).send('User role updated');
});In this example, the server blindly trusts that the request is legitimate, potentially allowing unauthorized actions.
How to Prevent CSRF Attacks in TypeScript ERP Systems
1. Implement CSRF Tokens
Generate a CSRF token for every session and validate it with each request.
Example: Adding CSRF Protection
import csrf from 'csurf';
import express from 'express';
const app = express();
const csrfProtection = csrf({ cookie: true });
app.use(csrfProtection);
app.get('/form', csrfProtection, (req, res) => {
res.render('form', { csrfToken: req.csrfToken() });
});
app.post('/submit', csrfProtection, (req, res) => {
res.send('Data is secure');
});Visualizing Vulnerability Assessments
Take advantage of our Free Website Security Scanner to identify vulnerabilities in your application. Here’s a screenshot showcasing its capabilities:
Additionally, here’s an example of a vulnerability assessment report generated for an ERP system using the tool:
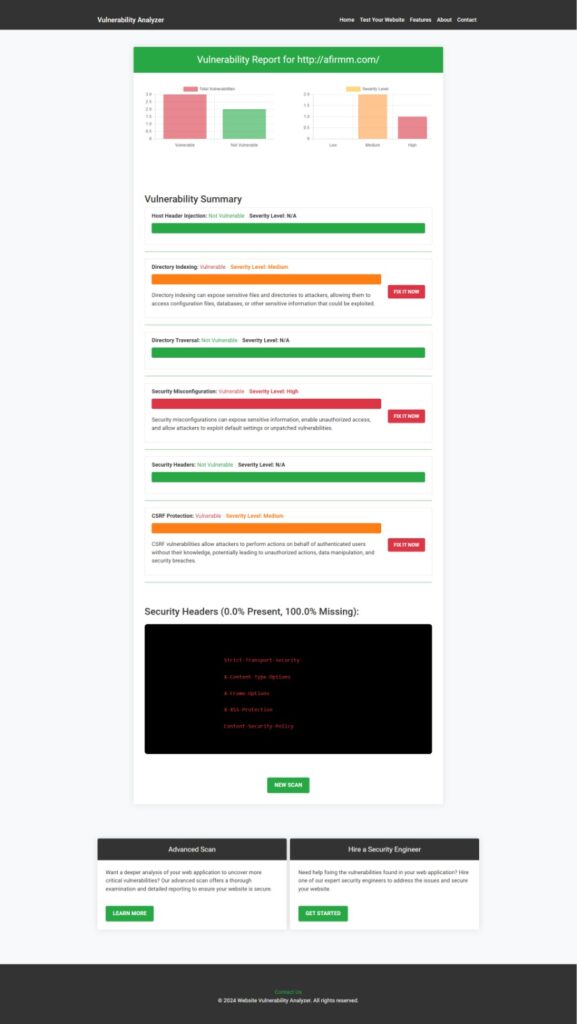
Linking Related Blogs for Better Context
For further insights on related security threats, explore our detailed blog on Cross-Site Scripting (XSS). You can also thank our team for sharing actionable security knowledge!
Strengthen ERP Security with Advanced Techniques
2. SameSite Cookies
Configure cookies with the SameSite attribute to prevent them from being sent with cross-origin requests.
Example: Setting SameSite Cookies
app.use(cookieSession({
name: 'session',
keys: ['key1', 'key2'],
cookie: {
httpOnly: true,
secure: true,
sameSite: 'strict',
},
}));3. Validate Referer Headers
Verify the Referer header to ensure requests originate from trusted domains.
Example: Referer Validation
app.post('/secureEndpoint', (req, res) => {
const referer = req.get('Referer');
if (!referer || !referer.startsWith('https://trusted.domain')) {
return res.status(403).send('Forbidden');
}
// Process the request
});Advanced Defense Strategies
- Content Security Policy (CSP) to block unauthorized resources.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to enhance user verification.
- Monitor Logs Regularly for suspicious activity.
Link to Other Resources
For additional guidance on securing your ERP, check out our in-depth guide on IDOR in OpenCart, 5 Crucial Fixes for IDOR in TypeScript-Based ERP.
Conclusion
CSRF attacks are a serious threat, especially for TypeScript-based ERP systems. By integrating CSRF tokens, leveraging SameSite cookies, and validating referrers, developers can significantly reduce vulnerabilities. Use tools like our Free Website Security Checker to detect and address issues proactively.
Stay tuned for more insights and guides on securing modern web applications!
Pingback: How to Fix Broken Authentication in OpenCart: 5 Proven Steps
Pingback: How to fix IDOR in TypeScript-Based ERP: Best 5 tips