5 Best Practices to Prevent HTTP Parameter Pollution in TypeScript ERP
Understanding HTTP Parameter Pollution in TypeScript ERP
HTTP Parameter Pollution (HPP) is a web vulnerability that arises when multiple HTTP parameters with the same name are sent in a single request.

In TypeScript-based Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, improper handling of such parameters can lead to unexpected behavior, security breaches, and unauthorized data access.
Attackers exploit HPP by injecting multiple parameters to manipulate application logic, bypass security controls, or access sensitive information.
How HTTP Parameter Pollution Occurs
In an HPP attack, an attacker sends multiple parameters with the same name in an HTTP request.
The server’s interpretation of these parameters can vary based on the application’s logic, leading to potential vulnerabilities.
Example of a Vulnerable Request:
GET /search?query=apple&query=bananaDepending on how the server processes these parameters, it might:
- Use the first parameter (
query=apple) - Use the last parameter (
query=banana) - Combine both parameters (
query=apple,banana)
This ambiguity can be exploited to alter application behavior maliciously.
Risks Associated with HTTP Parameter Pollution
HPP can lead to several security issues, including:
- Authentication Bypass: Manipulating parameters to bypass authentication mechanisms.
- Access Control Violations: Gaining unauthorized access to restricted resources.
- Data Manipulation: Altering data by injecting unexpected parameters.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Injecting scripts through polluted parameters.
Understanding these risks is crucial for developers to implement effective preventive measures.
5 Best Practices to Prevent HTTP Parameter Pollution in TypeScript ERP
Preventing HPP in TypeScript-based ERP systems involves adopting secure coding practices and proper input handling. Below are the top five best practices:
1. Implement Strict Input Validation
Ensure that your application validates all incoming parameters, allowing only expected parameters and rejecting duplicates.
Example in TypeScript:
import express, { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
const app = express();
function validateParameters(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
const allowedParams = ['username', 'password'];
const receivedParams = Object.keys(req.query);
for (const param of receivedParams) {
if (!allowedParams.includes(param)) {
return res.status(400).send('Invalid parameter detected.');
}
}
next();
}
app.use(validateParameters);
app.get('/login', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
res.send('Login successful.');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running on port 3000');
});In this example, the middleware validateParameters checks for unexpected parameters and rejects the request if any are found.
2. Utilize Parameter Parsing Libraries
Use libraries that handle parameter parsing securely, ensuring that duplicate parameters are managed appropriately.
Example with qs Library:
import express, { Request, Response } from 'express';
import qs from 'qs';
const app = express();
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.post('/search', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
const body = qs.parse(req.body);
res.send(`Search results for: ${body.query}`);
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running on port 3000');
});The qs library parses the parameters into an object, handling duplicates according to its configuration.
3. Enforce Unique Parameter Names
Design your API endpoints to accept unique parameter names, rejecting requests with duplicate parameters.
Example in TypeScript:
import express, { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
const app = express();
function checkForDuplicateParams(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
const params = new Set(Object.keys(req.query));
if (params.size !== Object.keys(req.query).length) {
return res.status(400).send('Duplicate parameters are not allowed.');
}
next();
}
app.use(checkForDuplicateParams);
app.get('/profile', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
res.send('User profile data.');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running on port 3000');
});This middleware checks for duplicate parameters and rejects the request if any are found.
4. Sanitize User Inputs
Remove or encode any unexpected characters from user inputs to prevent malicious data from affecting application logic.
Example in TypeScript:
function sanitizeInput(input: string): string {
return input.replace(/[^\w\s]/gi, '');
}
// Usage
const userInput = sanitizeInput(req.query.username as string);This function removes any non-alphanumeric characters from the input, reducing the risk of injection attacks.
5. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Regularly test your application for vulnerabilities, including HPP, using automated tools and manual testing.
Utilize free tools available at https://free.pentesttesting.com/ to perform comprehensive security assessments.
Example of Integrating Security Testing in Development Workflow:
# Install security testing tool
npm install -g security-tool
# Run security tests
security-tool scan --url http://localhost:3000Incorporating security testing into your development process helps identify and mitigate vulnerabilities early.
Visual Demonstration of Security Tools
To assist in identifying and mitigating HTTP Parameter Pollution vulnerabilities, consider using our free tools for a Website Security test.
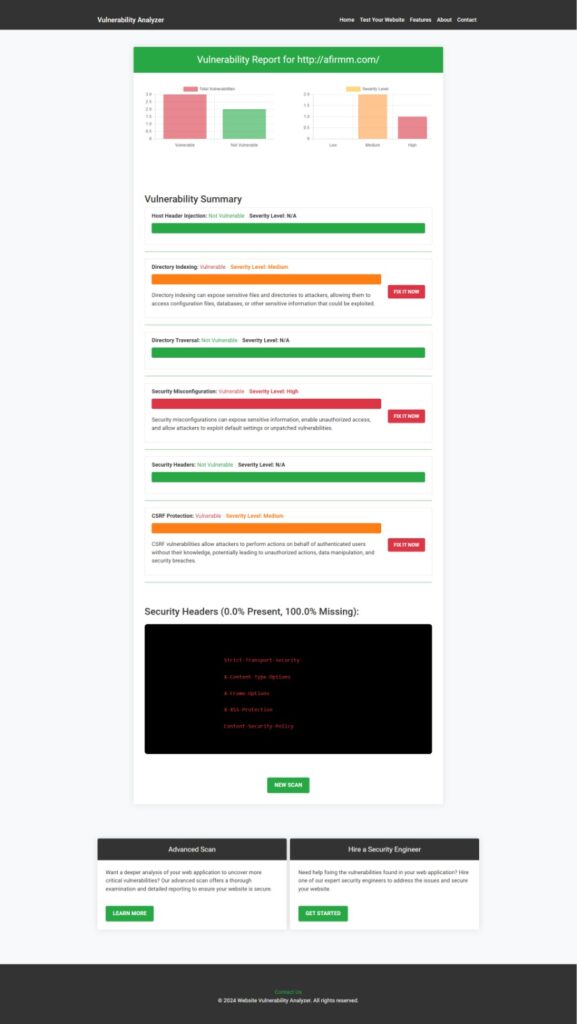
Additionally, after scanning your website with our free tool to check Website Vulnerability, you can generate a website vulnerability assessment report to get insights into security flaws.
Additional Resources
For more security tips and best practices, check out our related articles:
- 🔗 Subdomain Takeover in TypeScript
- 🔗 Prevent LDAP Injection in TypeScript ERP
- 🔗 Prevent CORS Misconfigurations in TypeScript
- 🔗 How to Prevent SQL Injection (SQLi) in Symfony
- 🔗 More Cybersecurity Insights
For securing OpenCart applications, check out our guide on Subdomain Takeover in OpenCart.
By following these best practices, developers can secure their TypeScript-based ERP systems against HTTP Parameter Pollution attacks and enhance overall application security. 🚀
Pingback: Prevent Business Logic Vulnerabilities in TypeScript: 7 Best