Best 7 Steps to Prevent Remote Code Execution RCE in TypeScript ERP
Remote Code Execution (RCE) is a critical security vulnerability allowing attackers to execute arbitrary code on a server. In TypeScript-based ERP systems, this vulnerability can lead to severe data breaches, financial loss, and reputation damage. This blog post explains RCE in TypeScript-based ERP systems, its implications, and how to secure your system with actionable steps and coding examples.

What is Remote Code Execution (RCE)?
Remote Code Execution is a vulnerability where attackers exploit system weaknesses to execute unauthorized commands. These vulnerabilities often stem from improper input validation, insecure configurations, or dependencies with known flaws. For TypeScript-based ERP systems, understanding how RCE works is vital to ensuring a secure architecture.
Common Causes of Remote Code Execution RCE in TypeScript-Based ERP Systems
- Unvalidated User Inputs: Not sanitizing inputs before processing.
- Improper Use of Dynamic Functions: For example, using
evalin TypeScript. - Insecure Dependencies: Using outdated libraries.
- Misconfigured Servers: Poor server-side settings leading to exploitation.
Step 1: Use Strong Input Validation
Input validation is your first line of defense. Below is an example of secure input validation in TypeScript:
function validateInput(input: string): string {
const regex = /^[a-zA-Z0-9-_]+$/;
if (!regex.test(input)) {
throw new Error("Invalid input detected!");
}
return input;
}
try {
const userInput = validateInput("test-input");
console.log(`Validated Input: ${userInput}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.message);
}By validating inputs, you can mitigate the risk of malicious payloads entering your system.
Step 2: Avoid Using eval and Similar Functions
Dynamic evaluation functions like eval should be avoided. Here’s why:
Bad Practice:
const userCode = "console.log('Hello, world!')";
eval(userCode); // Unsafe, vulnerable to RCESecure Alternative:
const userCode = "console.log('Hello, world!')";
// Process using safe and predefined logic
console.log(`Executing code: ${userCode}`);Step 3: Secure Dependency Management
Regularly audit dependencies in your TypeScript ERP system. Use tools like npm audit:
npm audit
npm audit fixFor example, ensure all libraries are updated:
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.18.3",
"typescript": "^4.9.4"
}
Step 4: Implement Secure Configuration Practices
Ensure your ERP servers are configured securely:
- Disable unused endpoints.
- Limit privileges for user roles.
- Configure Content Security Policies (CSP).
Free Website Security Checker Tool
Explore our free Website Security Scanner Tool to identify vulnerabilities like RCE. Below is an example of how the tool works in real time.
Step 5: Use Advanced Testing Mechanisms
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools can uncover hidden vulnerabilities. Use tools like OWASP ZAP for testing TypeScript ERP systems.
Vulnerability Assessment Report
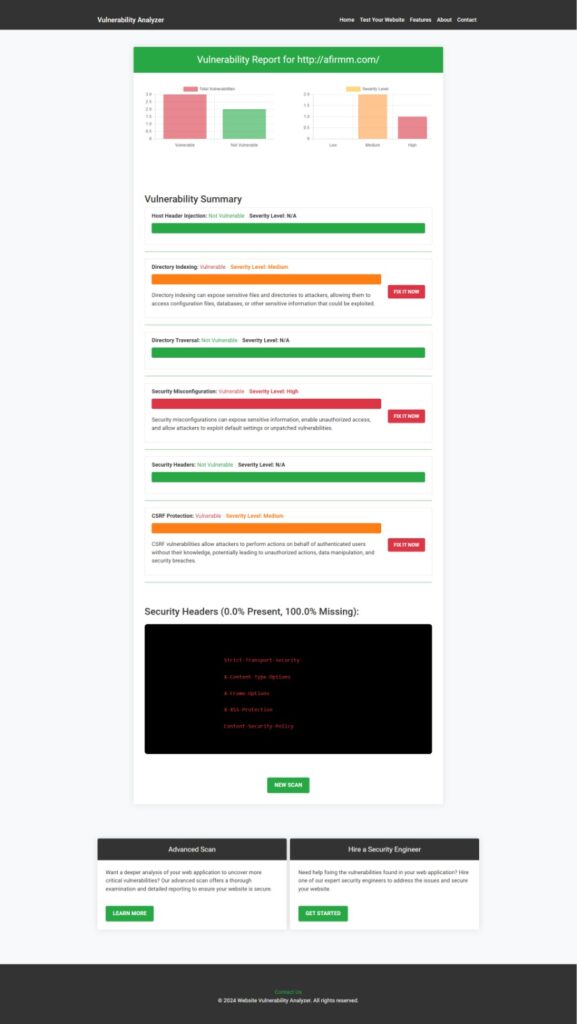
A sample Website Vulnerability Assessment Report generated by our free tool showcases how RCE risks are detected and mitigated.
Step 6: Link to Related Blogs and Topics
To dive deeper into related vulnerabilities, check out our blogs:
- Prevent Broken Access Control in TypeScript
- Fix Broken Authentication in TypeScript ERP
- Best 7 Tips to Prevent SSRF in TypeScript ERP
- Explore All Blogs
Also, learn about Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) in OpenCart to understand a different perspective on securing web applications.
Step 7: Educate Your Team
Train your developers on secure coding practices to reduce RCE vulnerabilities. Adopt tools like ESLint and Prettier for consistent and secure code formatting.
Conclusion
Remote Code Execution (RCE) is a critical risk in TypeScript-based ERP systems. However, with strong input validation, secure configurations, and regular testing, you can safeguard your ERP system. Explore our tool to test website security free to assess your system and take proactive measures today.
Pingback: How to Prevent SSRF in TypeScript ERP Systems: Best 7 Tips